Functional chemical vapour deposition
Thin films on bulk materials such as glass, metal or plastics can give functional properties such as infection control, self-clean, conductive, light trapping, anti-reflection, or surface wettability.
Infection control – Silver and copper have been known as far back as 2600 BC for their anti-microbial properties. By incorporating these with other materials (e.g. silica or titanium dioxide) for increased hardness and additional self-cleaning we have shown their abilities to kill a range of different types of bacteria or combined functionality.
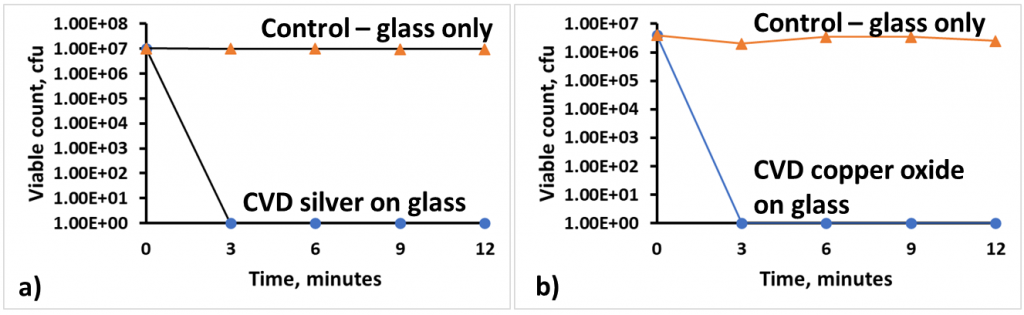
Viable cell count for E coli on FACVD silver and copper oxide
The persistence of pathogenic, antibiotic-resistant bacteria in hospitals, alongside the ongoing COVID-19 pandemic, shows how rapidly micro-organisms can spread from contaminated surfaces as well as between people. At Salford there is a cross-disciplinary grouping, including Salford Royal Foundation Trust, all working towards solving these issues.
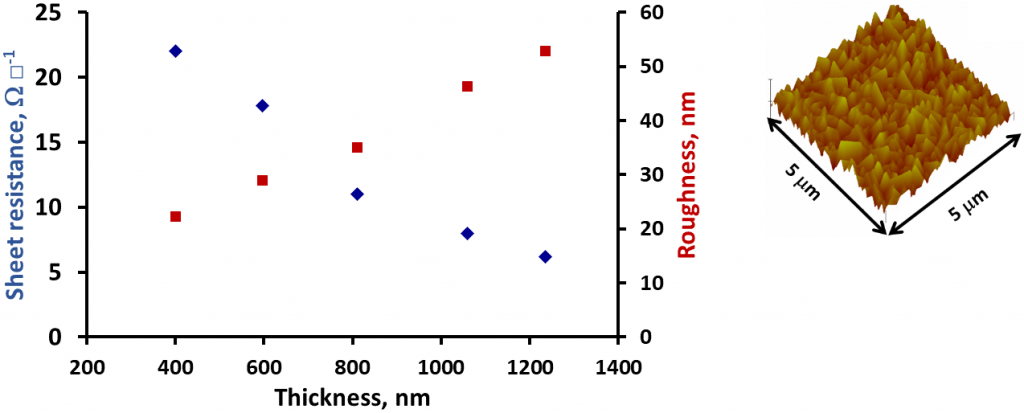
Conductive – Doped tin oxide and zinc oxide have been used as electrodes in photovoltaics. By tailoring the surface structure and roughness it was possible to increase light trapping and hence improved device performance. In addition, layers of dense, pinhole free titania or porous nickel oxide have been used as efficient charge carriers in other cell types.
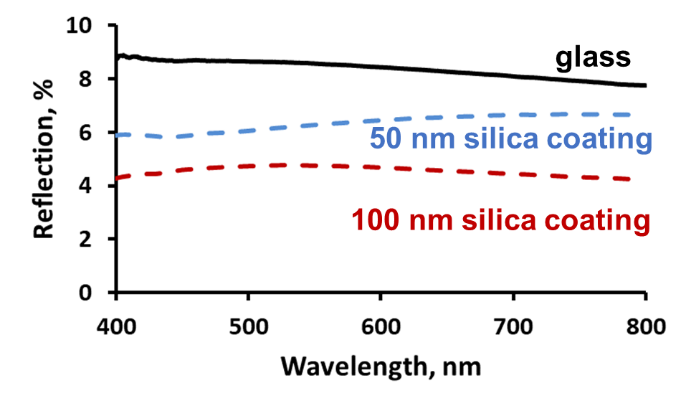
Anti-reflection – Controlling the porosity, which modifies the refractive index, and thickness of a thin film alters the extent of light interference and hence what wavelengths of light are reflected, so modifying the coatings anti-reflection performance.
Surface wettability – Hydrophobic behaviour can be obtained in CVD deposited coatings, whether polymeric or surface structured to follow the ability of lotus leaves to shed water. Alternatively, a coating can be made controllably hydrophobic to hydrophilic under UV light due to photocatalytic activity.
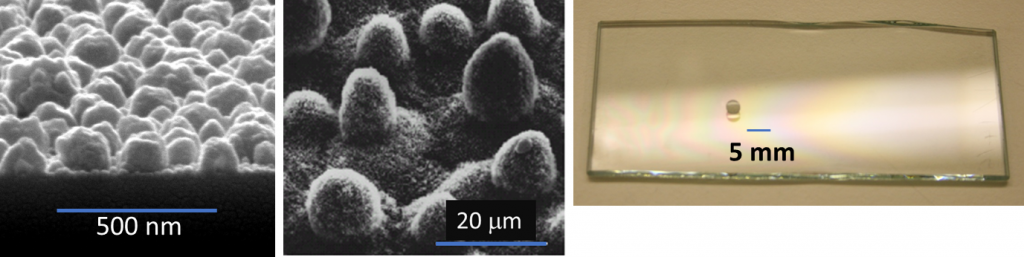
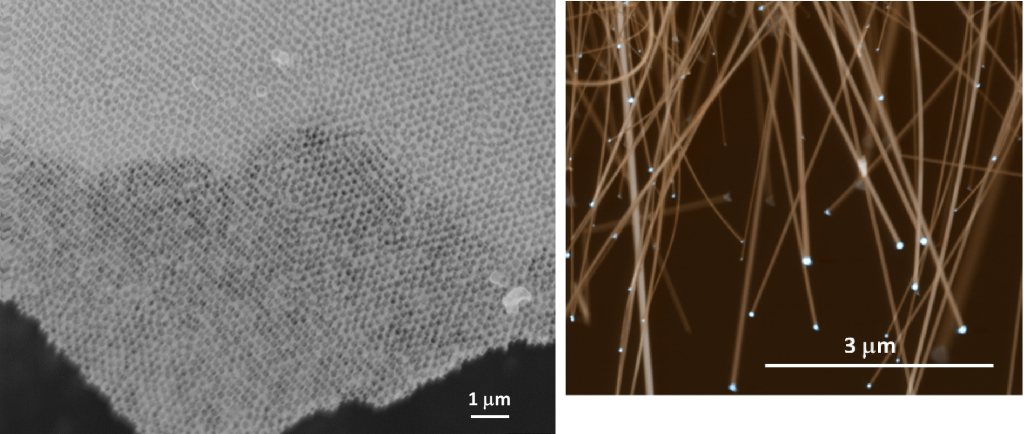
Coatings do not just have to be on flat surfaces, at Salford, we have deposited III-V semiconductors in 3D structures to give opalescent structures with full photonic bandgaps or by use of gold nano-dots catalysts formation of 2D silicon wires.